An array is a linear
collection of finite number of homogeneous data elements that store
in a successive memory locations.
Size of array
In case start index
zero.
size=Upper Bound-Lower
Bound+1
In case start index one.
size=Upper Bound
TYPES OF ARRAY
One dimensional array
Two dimensional array
Multi dimensional array
ONE DIMENSIONAL ARRAY
One dimensional array is
a array in which each element of array refer by single or one
subscript.
Example:-A[1],A(1)
TWO DIMENSIONAL ARRAY
Two dimensional array is
array in which each element of array is refer by two subscript.Two dimensional
array structure require to store data in a form of table.
Example:-A[1,2],A(1,2)
MULTI DIMENSIONAL ARRAY
Multidimensional array
is array in which each element of array reffer by two or more subscript.
Example:-A[1].......A[n];
LINEAR ARRAY
A linear array is a list
of a finite number n of homogeneous data elements such that the elements of the
array are stored in successive memory locations.
Ex:-A[4].
Upper Bound is the
largest index.
Lower Bound is the
smallest index.
Formula:- Length=Upper
Bound-Lower Bound+1
Let LA be a linear array
in the memory of the computer.The element of linear array are stored in
consecutive memory locations.The computer does not keep track of address of
each element of array.It only keeps track of the base address of the array. We
can find out the location of any element by using formula and example:
LOCATION(LA[k])=Base(LA)+W(K-LB)
LOCATION(LA[K]) is the
location of the K element LA.
W is the number of bytes
taken by one element.
K is the K
element.
LB is the lower bound.
Example:-Location(A[3])=1000+2(3-1) :=1000+2(2):=1004
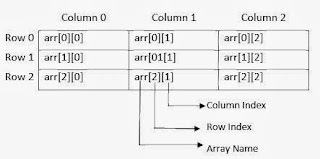
TWO DIMENSIONAL ARRAY
Two dimensional array is
array in which each element of array is refer by two subscript.Two dimensional
array structure require to store data in a form of table.Ex:-A[1,2],A(1,2)
A two-dimensional m*n
array A is a collection of m.n data elements such that each element is
specified by a pair of integers(j,k).
Example:-A[3][3];
REPRESENTATION OF
TWO-DIMENSIONAL ARRAY IN MEMORY
Memory representation of
a 2-D array is different from the linear array.Specifically,the programming
language will store the array A either (1) column by column is called
column-major order and(2) row by row,is called row-major
order.Let A[3][3].
ROW MAJOR ORDER
TO FIND ADDRESS
Formula:-
LOCATION(A[J.k])=Base(A)+w[N(J-1)+(K-1)]
COLUMN MAJOR ORDER
TO FIND ADDRESS
Formula:-
LOCATION(A[J,K])=Base(A)+w[M(K-1)+(J-1)]

Comments
Post a Comment